Galileo upgrade is now live
Dec 15, 2025 · 4 min read

Galileo upgrade is now live
tldr
Galileo adapts Scroll to Fusaka, enables support for the latest Solidity version 0.8.31. Reduces zkVM cycles by 50% through prover optimizations. Introduces a new fee structure that keep transaction fees low while implementing anti-spam measures, and prepares to migrate from l2-geth to l2-reth.
Galileo, the third major Scroll upgrade this year, went live on Scroll Sepolia on November 25th, 2025, with a Mainnet launch on December 16th. This release ensures compatibility with the latest Ethereum changes, significantly optimizes ZK proving, and introduces a more robust fee structure.
Full EVM Compatibility
Scroll has rapidly mirrored the EVM execution changes introduced by Ethereum’s Fusaka hardfork so developers can keep having the same experience as in Ethereum.
Execution protocol updates include:
secp256r1precompile: Introduced in a prior Scroll upgrade, this precompile allows users to sign in via iPhone, Android, TEEs, and other devices. In this upgrade, its gas calculations were revised to match its inclusion in the Fusaka hardfork.MODEXPprecompile: New limits and gas formula adjustments were applied to the exponentiation precompile to prevent prover killer spikes when trying to calculate large exponents. This provides better predictability for Scroll prover hardware even in worst case scenarios.CLZopcode: Adding this new opcode ensures Scroll is compatible with the latest Solidity version0.8.31. Significant prover optimizations can be achieved when developers use this opcode in their smart contracts. This happens automatically at the compiler level when using the latest compiler versions, meaning developers can use existing code without change.
New Rollup Fee Structure
Galileo implements a new fee calculation that makes Scroll more robust and adaptable while keeping very low transaction fees for users.
The new formula introduced by Galileo is the following:

Where the components are defined as:

This structure divides fees into two components. The base term is linear in relation to the compressed size and accurately accounts for the direct transaction costs. The penalty term is quadratic in relation to the compressed size and penalizes large transactions that cause DA inefficiencies. This design adapts to future changes in L1 gas fee calculations and blob fees following the recent BPOs schedule. At the protocol level, two variables decouple the L1 costs. The commit_scalar includes both L1 commit and execution costs, while blob_scalar covers blob costs.
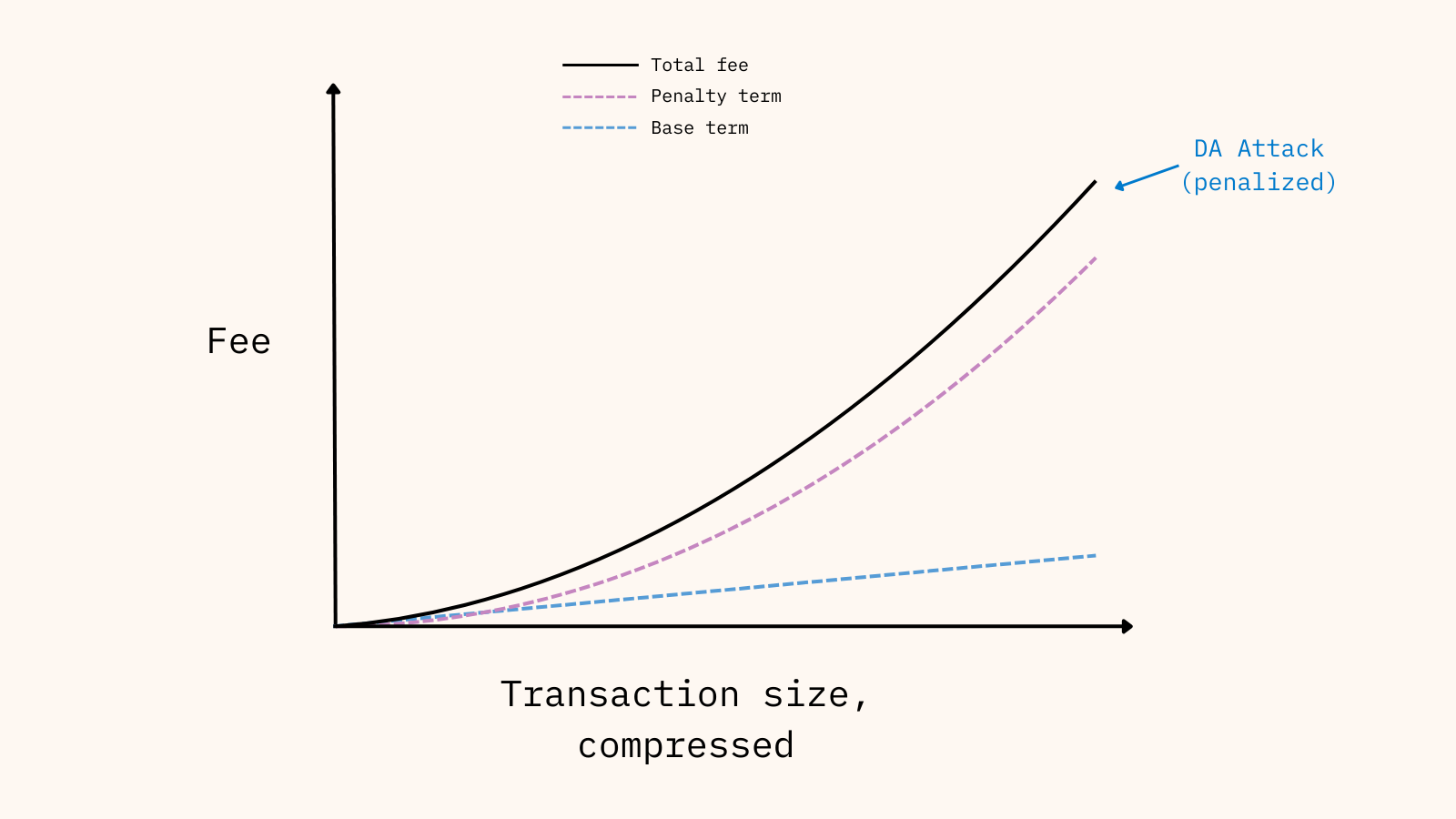
The new formula maintains low fees for honest users while imposing quadratic penalties on attackers based on transaction size.
Additionally, we have introduced a new penalization formula for unusual transaction sizes to mitigate spam attacks. With Scroll’s transaction costs now significantly lower, a new vector emerged allowing malicious actors to force unnecessary L1 blob fees by intentionally sending transactions with excessive calldata. The new formula increases fees quadratically for abusive transactions, disincentivizing attackers while maintaining low costs for honest users.
Prover and Infrastructure Optimizations
The upgrade features very important behind-the-scenes changes for performance at the sequencer and prover level.
Prover optimization has resulted in a ~50% reduction in ZK proving cycles. This was achieved by restructuring the MPT circuit reconstruction logic. A new memoization mechanism, inspired by Risc0, replaces on-the-fly Merkle path recalculation with a deterministic caching system. The network has also been upgraded to OpenVM v1.4.1 for additional performance improvements.
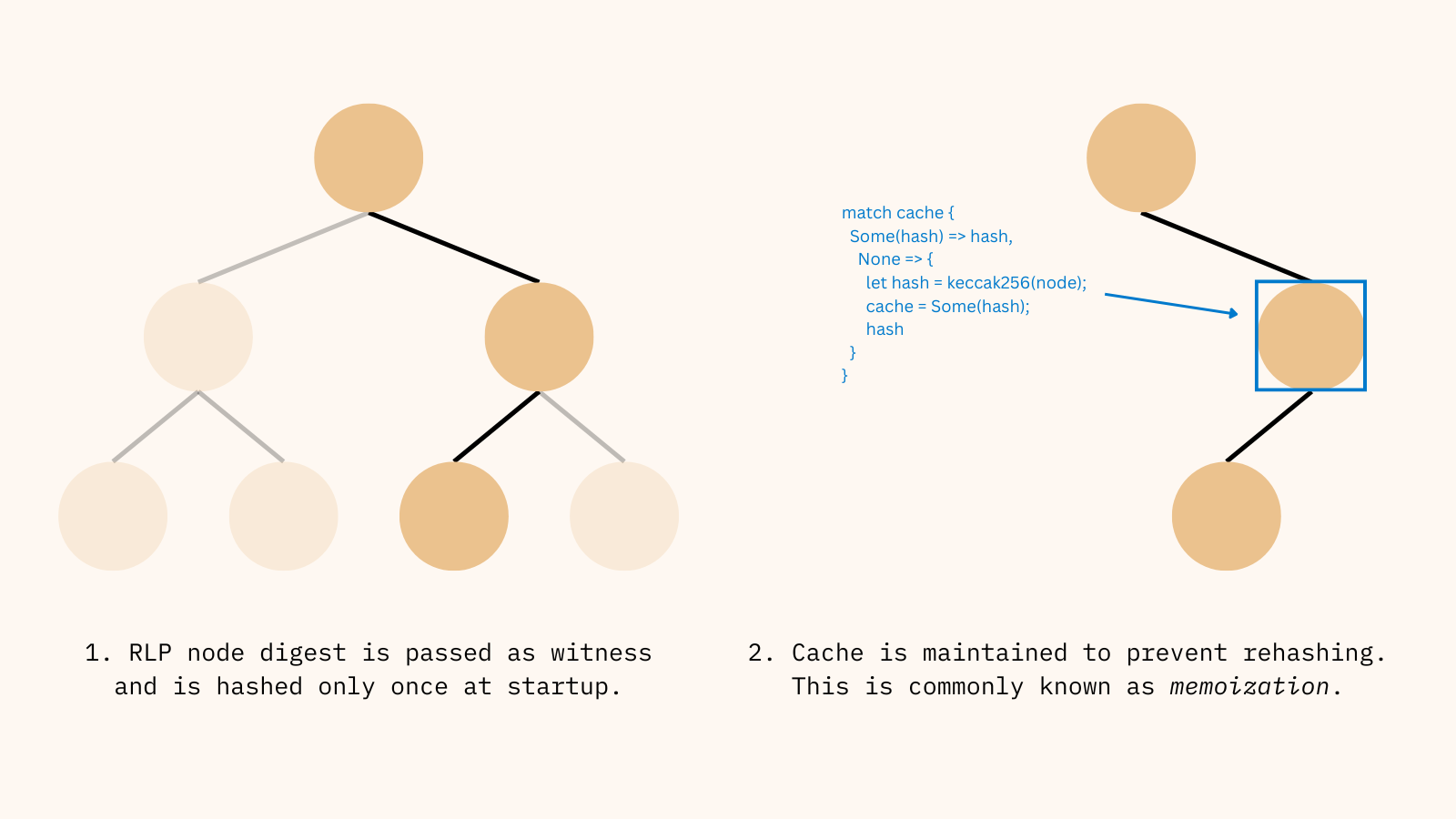
The new MPT cache system plus OpenVM upgrade reduces zkVM cycles by about 50%
Additionally, Scroll is transitioning its node client from l2-geth to l2-reth. This infrastructure migration, tested alongside all the Galileo changes, will benefit from a more performant and lightweight client for node operators.
To know more about this upgrade please visit the the upgrade announcement in the governance forum.